Assessment and Examination
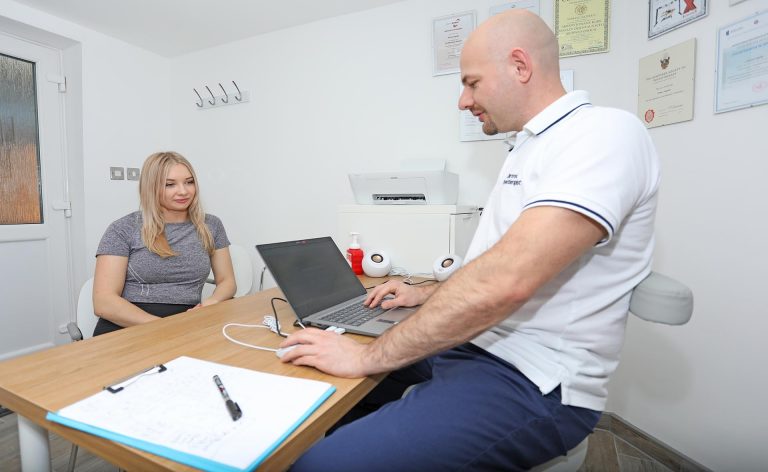
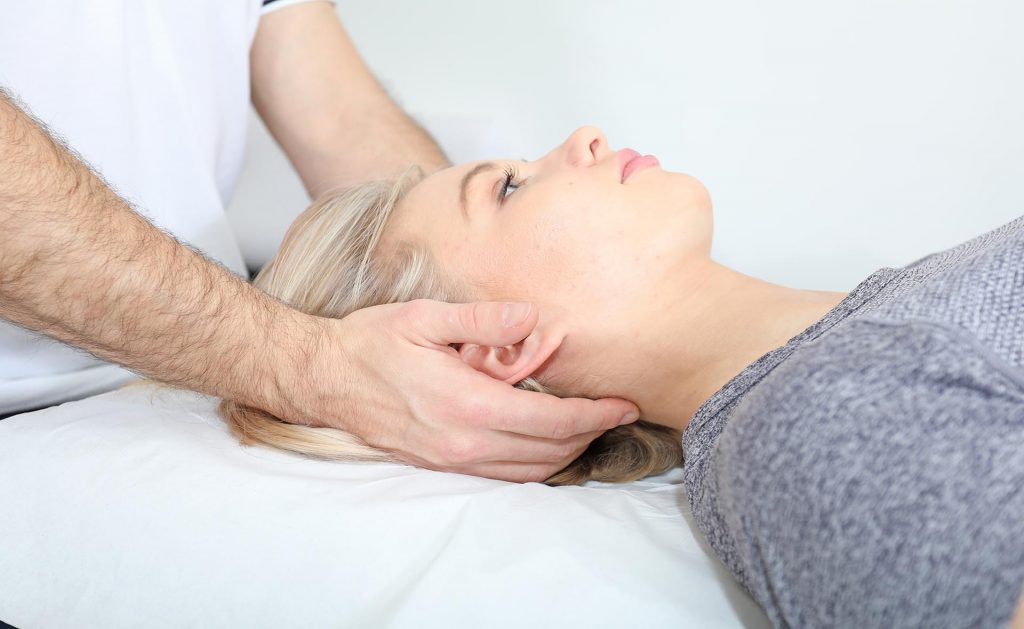
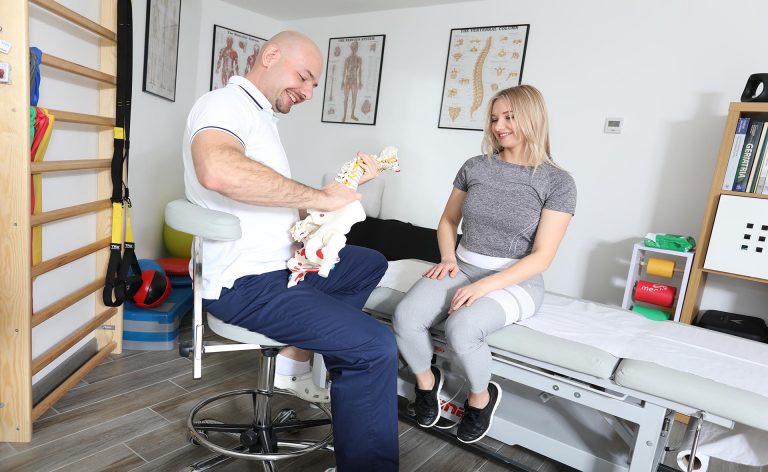
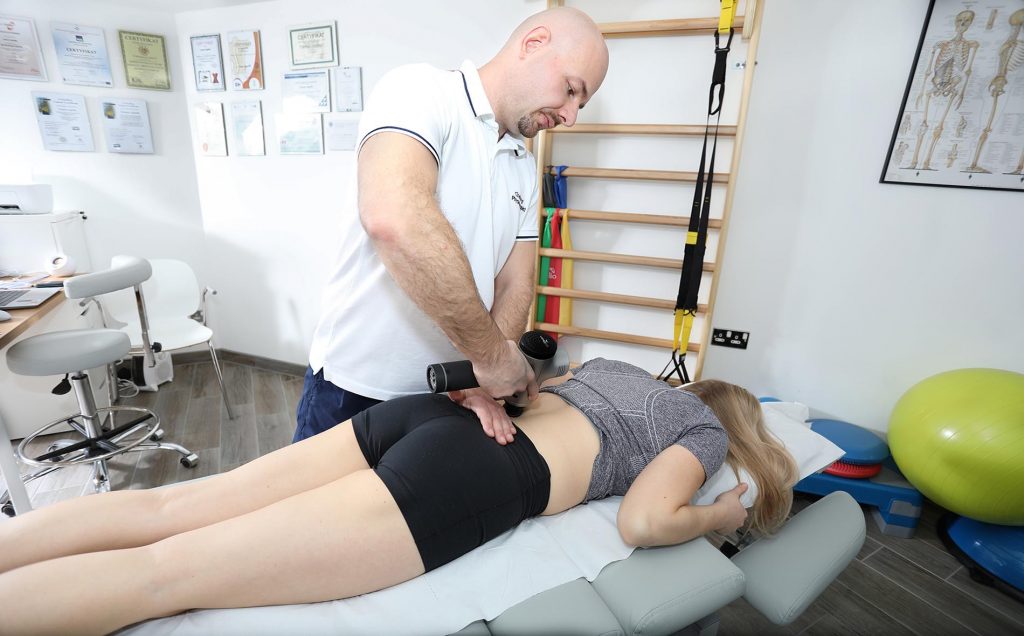
The first contact with a patient is a diagnostic element. A physical therapist will conduct an evaluation and examination to diagnose and understand your injury. He will start the observation from the moment you enter the office – he will analyze the gait movement, thanks to which he will be able to identify possible dysfunctions. Thanks to a specialist interview, relative and absolute contraindications for the therapy can be established. After a thorough examination, the therapist will develop a treatment plan to help you overcome this injury.
Physio Assessment and Examination
The physiotherapist is responsible for the patient’s eligibility for rehabilitation. They have the experience and competence to carry out physiotherapeutic diagnostics. It is a process consisting of:
- Interview
- Posture Assessments and Movement Analysis
- Tests and measurements
- Making a diagnosis and discussing it with the patient
- A treatment plan and predictions for the future
A professionally conducted interview gives answers to questions such as: What problem has the patient had? What hurts and why? Since when have the symptoms persisted? How did this happen? What are the comorbidities? This points to the mechanism of the injury and outlines how to approach the problem. A lot of musculoskeletal problems can be deduced based on the interview itself. Possible symptoms that signal severe disorders, i.e. “red flags,” e.g. cancer, will be picked up. Should the need be, the therapist sends the patient to their primary care physician for a more in-depth diagnosis.
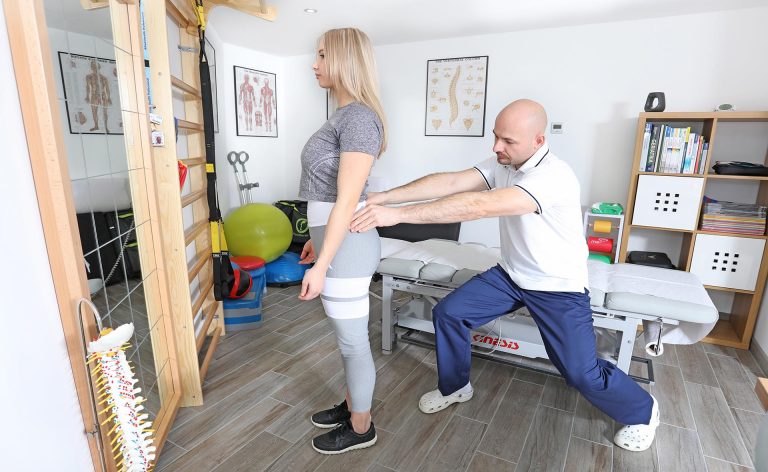
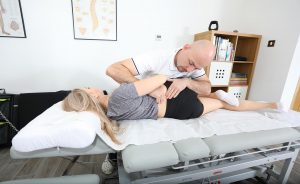
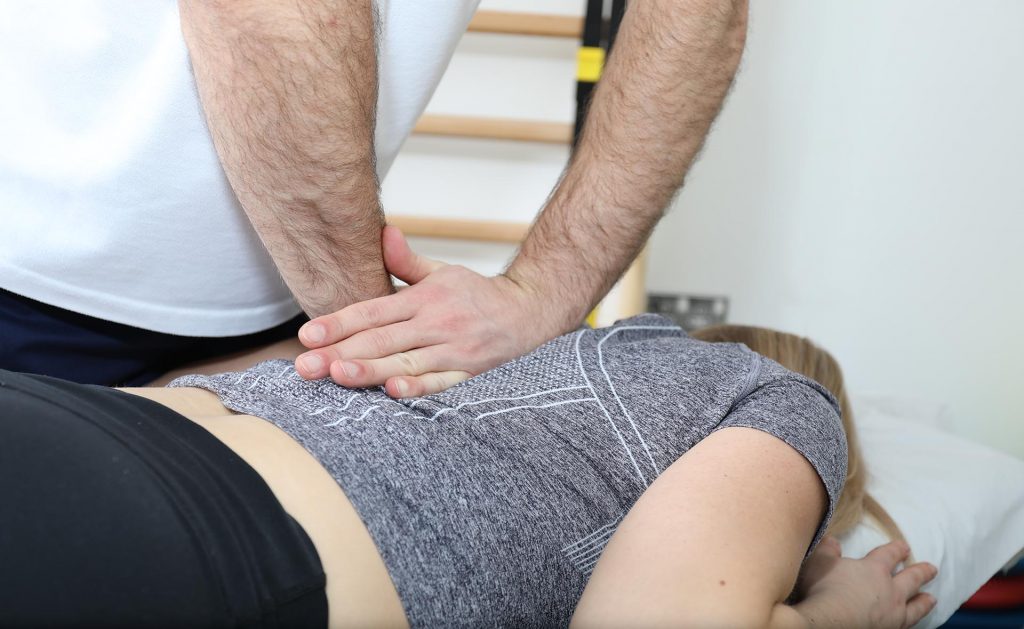
The physical examination and taking medical history are based on assessing body posture and motor skills, examining reflexes, muscle strength and tension, or the range of movements in the joints. If necessary, linear measurements are done (limb length and circumference). Patient pain assessment, e.g. with the VAS 0-10 scale. Thanks to the analysis of functional movement disorders and the information provided by the patient, special orthopaedic and neurological tests are selected, which confirm the assumed diagnosis, and then the final diagnosis is made.
It is essential to discuss and explain the test results with the patient. The patient’s knowledge about their problem is of great importance, as the patient’s awareness affects the effects of rehabilitation. The improvement plan takes into account the patient’s motivation and capabilities. Stages are outlined to achieve the intended result. We adjust the method of therapy when we receive all this information.
Recommendations are an essential element in the rehabilitation process. The therapist gives tips on correct ergonomics, self-therapy, or home exercises.
Book your appointment
What physiotherapeutic tests does a physiotherapist perform?
For the needs of local physiotherapy, our specialist performs dynamic and static tests.
Static test:
- Linear measurements of limb length – are made with a centimeter tape. The test items should be stable and comfortable for both the patient and the physiotherapist. Measurements are performed on both sides, starting from the healthy limb, and the lengths are divided into total, segmental, absolute and relative lengths.
- Circumference measurements – the increase or decrease in muscle mass is assessed, as well as possible exudative changes in the joints. The test is carried out with a centimeter tape. Circuit changes are often dynamic, so measurements are made every few days.
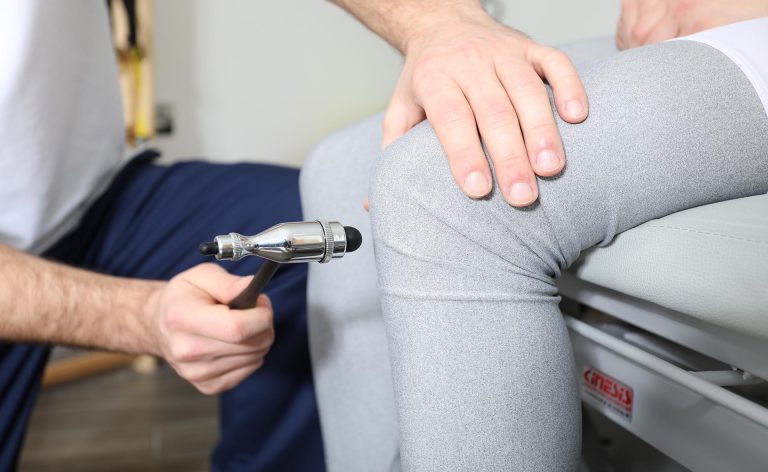
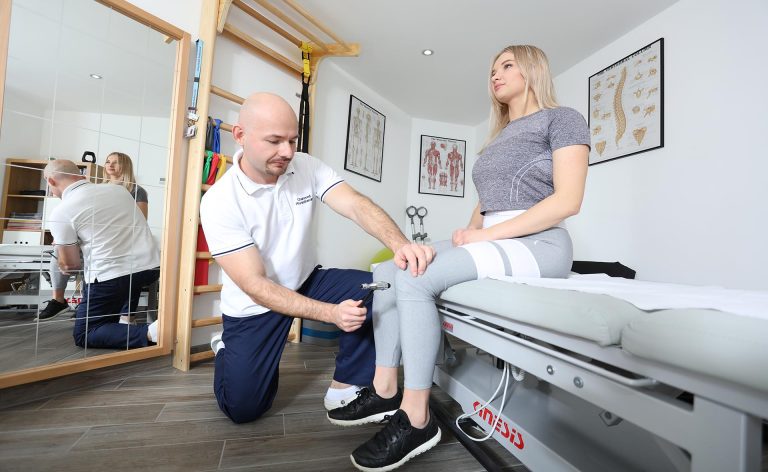
- Examination of the receptive part of the nervous system – such a study is carried out in the case of neurological diseases. Surface, deep and cortical receptors are examined.
Dynamic testing:
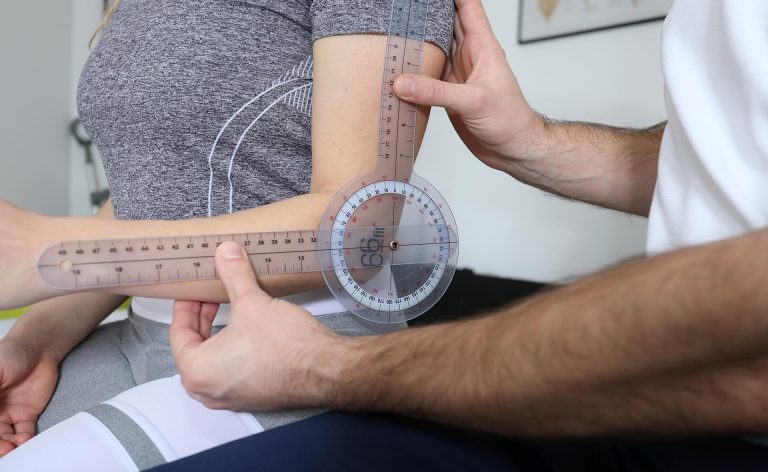
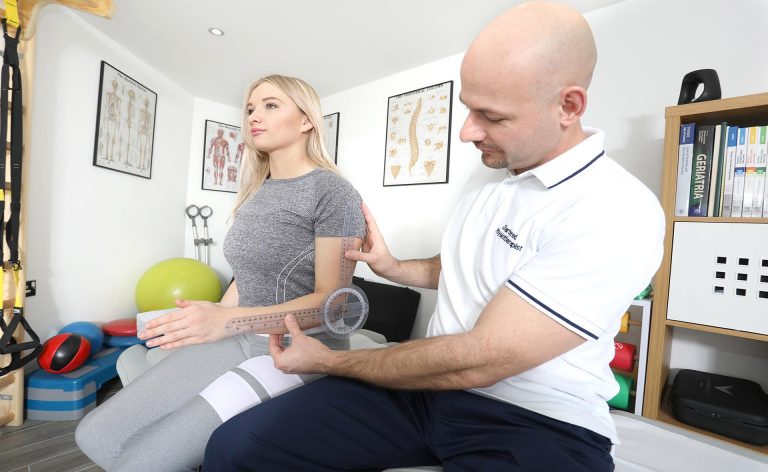
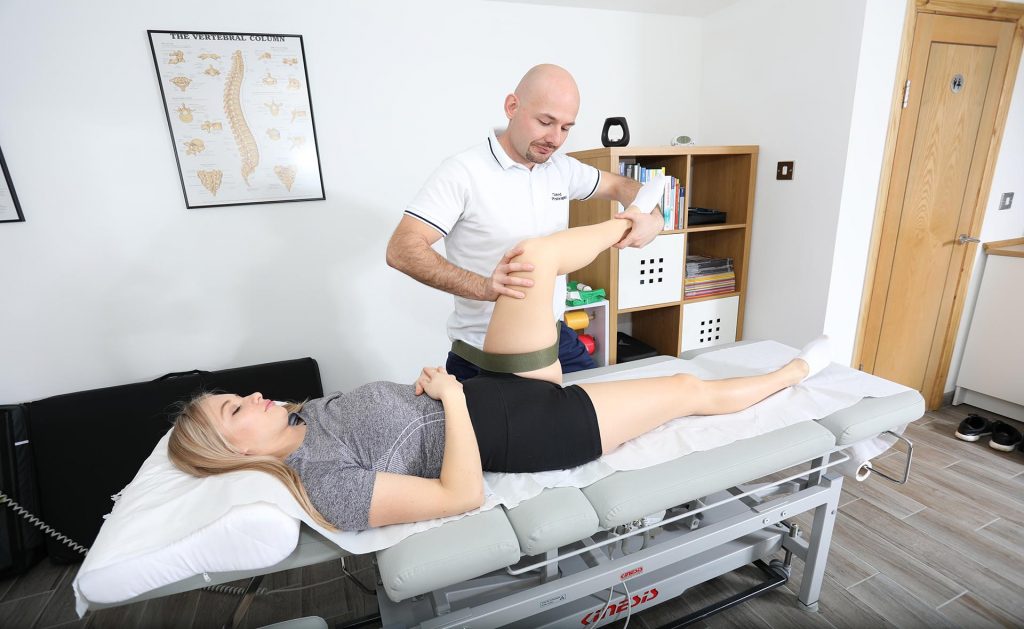
- Tests in the field of mobility – are performed using a goniometer. The range of mobility may be active or passive, it is often measured roughly, e.g. when examining the lumbar spine, a physiotherapist orders the patient to perform a toe-to-floor test.
- Assessment of muscle strength – the physiotherapist performs the examination using the Lovett test. The starting position and resistance depend on the functional state of the patient. The test has a 6-step scale, where 0 means no muscle contraction and 5 means the strength is correct for specific muscle groups to contract.
- Functional tests – tests designed to evaluate a given part of the body. It can be an Otto test for spine mobility in the thoracic section or an Apley test for meniscal damage.
Book your appointment
Physiotherapeutic examination
Physiotherapeutic treatments are carried out by a specialist with many years of practical experience and current knowledge in the field of rehabilitation. Knowing each muscle, tendon and joint, as well as its range of motion, it is able to correctly assess the scale of the injury and select specific treatment so that the body returns to full fitness and mobility as soon as possible. Neurological examinations and functional tests are performed using modern equipment.
Physiotherapeutic consultation allows you to assess the patient’s condition, diagnose the cause of chronic pain or develop a treatment for an injury. The purpose of the consultation is to analyse the problem, and additional tests may be ordered if necessary. Diagnostic tests make it possible to select the appropriate treatment so that the patient can travel from rehabilitation to full fitness in the shortest possible time.